Tevatron scientists announce their final results on the Higgs particle
 |
The CDF and DZero collaborations have found their strongest indication to date for the long-sought Higgs particle.
|
After more than 10 years of gathering and analyzing data produced by the U.S. Department of Energy's Tevatron collider, scientists from the CDF and DZero collaborations have found their strongest indication to date for the long-sought Higgs particle. Squeezing the last bit of information out of 500 trillion collisions produced by the Tevatron for each experiment since March 2001, the final analysis of the data does not settle the question of whether the Higgs particle exists, but gets closer to an answer. The Tevatron scientists unveiled their latest results on July 2, two days before the highly anticipated announcement of the latest Higgs-search results from the Large Hadron Collider in Europe.
"The Tevatron experiments accomplished the goals that we had set with this data sample," said Fermilab's Rob Roser, cospokesperson for the CDF experiment at DOE's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. "Our data strongly point toward the existence of the Higgs boson, but it will take results from the experiments at the Large Hadron Collider in Europe to establish a discovery."
Scientists of the CDF and DZero collider experiments at the Tevatron received a round of rousing applause from hundreds of colleagues when they presented their results at a scientific seminar at Fermilab. The Large Hadron Collider results will be announced at a scientific seminar at 2 a.m. CDT on July 4 at the CERN particle physics laboratory in Geneva, Switzerland.
"It is a real cliffhanger," said DZero co-spokesperson Gregorio Bernardi, physicist at the Laboratory of Nuclear and High Energy Physics, or LPNHE, at the University of Paris VI & VII. "We know exactly what signal we are looking for in our data, and we see strong indications of the production and decay of Higgs bosons in a crucial decay mode with a pair of bottom quarks, which is difficult to observe at the LHC. We are very excited about it."
The Higgs particle is named after Scottish physicist Peter Higgs, who among other physicists in the 1960s helped develop the theoretical model that explains why some particles have mass and others don't, a major step toward understanding the origin of mass. The model predicts the existence of a new particle, which has eluded experimental detection ever since. Only high-energy particle colliders such as the Tevatron, which was shut down in September 2011, and the Large Hadron Collider, which produced its first collisions in November 2009, have the chance to produce the Higgs particle. About 1,700 scientists from U.S. institutions, including Fermilab, are working on the LHC experiments.
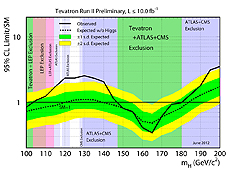
The Tevatron results indicate that the Higgs particle, if it exists, has a mass between 115 and 135 GeV/c2, or about 130 times the mass of the proton.
"During its life, the Tevatron must have produced thousands of Higgs particles, if they actually exist, and it's up to us to try to find them in the data we have collected," said Luciano Ristori, co-spokesperson of the CDF experiment and physicist at Fermilab and the Italian Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) . "We have developed sophisticated simulation and analysis programs to identify Higgs-like patterns. Still, it is easier to look for a friend's face in a sports stadium filled with 100,000 people than to search for a Higgs-like event among trillions of collisions."
Read more
|